工程醛脱氢酶酰胺键形成
近日,北京大学雷晓光团队研究了工程醛脱氢酶酰胺键形成。相关论文于2026年1月29日发表在《科学》杂志上。
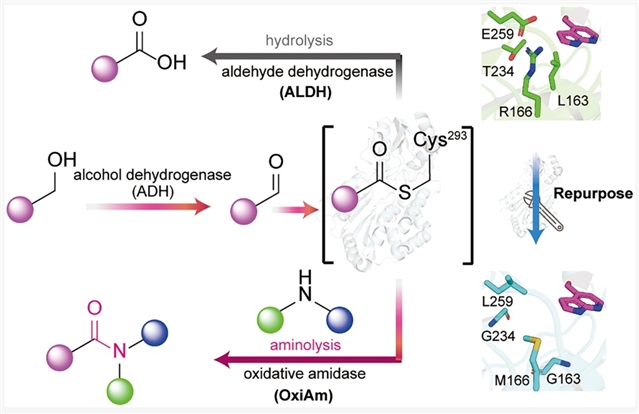
酰胺键形成反应在药物合成中应用广泛,传统方法通常需要化学计量偶联试剂来活化羧酸底物进行缩合反应。
作为替代策略,研究组通过改造醛脱氢酶,构建了更具疏水性与空间扩展性的催化口袋,使胺类化合物能够捕获硫酯中间体,从而将醛脱氢酶转化为氧化酰胺酶。该生物催化剂能高效促进多种醛与胺之间的酰胺键形成。
研究组还开发了两步酶级联反应,利用广泛存在的脂肪醇合成酰胺化合物。这一生物催化策略成功实现了五种药物分子合成路线的重新设计。该研究彰显了氧化酰胺酶通过高效构建酰胺键来推进结构多样性药物分子合成的潜力。
附:英文原文
Title: Engineered aldehyde dehydrogenases for amide bond formation
Author: Lei Gao, Xiang Qiu, Jun Yang, Kangdelong Hu, Peilin Li, Wei Li, Feng Gao, Fabrice Gallou, Florian Kleinbeck, Xiaoguang Lei
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-29
Abstract: Amide bond formation is widely used in pharmaceutical synthesis, typically involving stoichiometric coupling reagents to activate carboxylic acid substrates for a condensation reaction. As an alternative approach, we repurposed aldehyde dehydrogenases into oxidative amidases by creating a more hydrophobic and spacious catalytic pocket for amines to capture the thioester intermediate. This biocatalyst efficiently facilitates the formation of amide bonds between diverse aldehydes and amines. We also developed a two-step enzymatic cascade to synthesize amides from broadly available aliphatic alcohols. This biocatalytic strategy enabled the redesign of synthetic routes for five drug molecules. Our findings highlight the potential of oxidative amidases in advancing the synthesis of structurally diverse drug molecules through efficient amide bond formation.
DOI: adw3365
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adw3365



